Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries are used in a wide variety of applications due to their light weight, high energy density, and flexible form factors. These batteries are popular across multiple industries, including consumer electronics, drones, remote control (RC) cars, and even in more specialized areas such as medical devices and electric vehicles. Here is a brief overview of some key LiPo battery applications:
UAVs and drones: LiPo batteries are essential for powering drones in both the consumer and industrial sectors. Their high energy density ensures longer flight times and supports heavier payloads, making them ideal for aerial photography, surveying, and delivery services. The compact design allows drones to be lighter and more agile, enhancing flight stability.
RC vehicles: LiPo batteries are commonly used in RC cars, boats, and aircraft, providing the necessary power for long-lasting, high-performance operations. Their high discharge rates allow for fast acceleration and quick response, which is essential for competitive racing or hobbyist activities.
Consumer electronics: LiPo batteries are used in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearables due to their slim and flexible form factors. They provide a lightweight, efficient power source that helps extend device battery life, making them ideal for portable electronics.
Electric Vehicles: Lithium polymer batteries are also used in electric vehicles (EVs), especially small applications such as e-bikes, scooters, and skateboards. They provide efficient, long-lasting energy while maintaining a compact size, which is critical to vehicle performance.
Medical Devices: In the medical field, lithium polymer batteries power devices such as hearing aids, portable medical devices, and even some advanced prosthetics. Their reliability, long life, and lightweight properties make them ideal for such sensitive and portable applications.

Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries consist of several key components that work together to provide an efficient, lightweight, and high-energy power source. Here is a breakdown of its major parts:
Anode (negative electrode): The anode is usually made of graphite and stores lithium ions during the battery discharge process. It plays a vital role in the overall performance and capacity of the battery.
Cathode (positive electrode): The cathode is usually made of lithium metal oxide or lithium iron phosphate. It releases lithium ions during discharge and is a key factor in determining the battery’s voltage and capacity.
Electrolyte: LiPo batteries use a gel-like polymer electrolyte that allows lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode. The gel format makes the battery more flexible and safer than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Separator: The separator is a thin, porous material that prevents the anode and cathode from contacting each other while allowing lithium ions to pass through. It helps prevent short circuits and ensures safe operation of the battery.
Casing: LiPo batteries are usually enclosed in a soft, flexible pouch made of aluminum or plastic. The casing allows for a lightweight design, and its flexibility allows the battery to be shaped for different applications.
Battery Management System (BMS): Although not part of the battery itself, the BMS is often integrated into lithium polymer batteries. It monitors the battery’s voltage, temperature, and charge cycles to ensure safety and prevent overcharging or deep discharge.
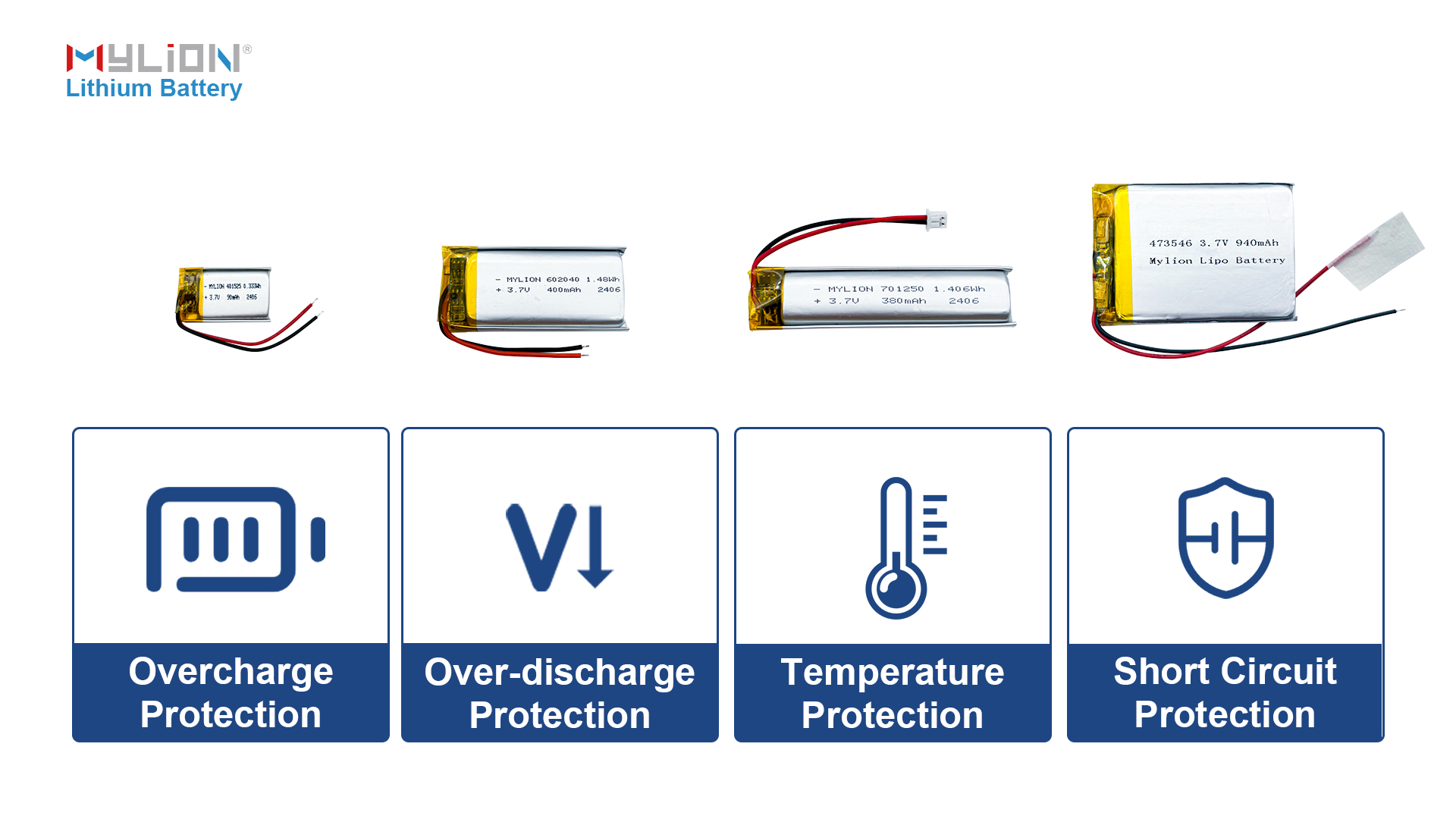
The battery management system (BMS) in lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, life, and performance of the battery. It monitors and protects the battery by performing several key functions:
Overcharge protection: The BMS prevents the battery from charging beyond its safe voltage limit. Overcharging can cause battery degradation, overheating, and even fire, so the BMS stops charging when the voltage reaches a preset threshold.
Overdischarge protection: It also prevents the battery from overdischarging, which can damage the battery and shorten its life. The BMS cuts off the load when the voltage falls below a certain level.
Overcurrent protection: The BMS monitors the current and prevents excessive current, which can cause overheating or internal damage. It ensures that the battery operates only within safe current limits.
Temperature monitoring: The BMS checks the temperature of the battery during charging and discharging. If the temperature is above or below the safe limit, it stops charging or discharging to protect the battery from thermal damage.
Balancing: In a multi-cell LiPo battery, the BMS ensures that all cells remain balanced by monitoring voltage levels. It ensures that no cell is overcharged or over-discharged relative to the others, improving performance and extending battery life.
Short Circuit Protection: The BMS detects a short circuit inside the battery and immediately cuts off power to prevent damage or fire risk.






